Bone remodelling Figure 23 shows the bone remodelling process with the Biology Diagrams bone remodeling, continuing process of synthesis and destruction that gives bone its mature structure and maintains normal calcium levels in the body. Destruction, or resorption, of bone by large cells called osteoclasts releases calcium into the bloodstream to meet the body's metabolic needs and simultaneously allows the bone—which is inhibited by its inorganic component from growing by

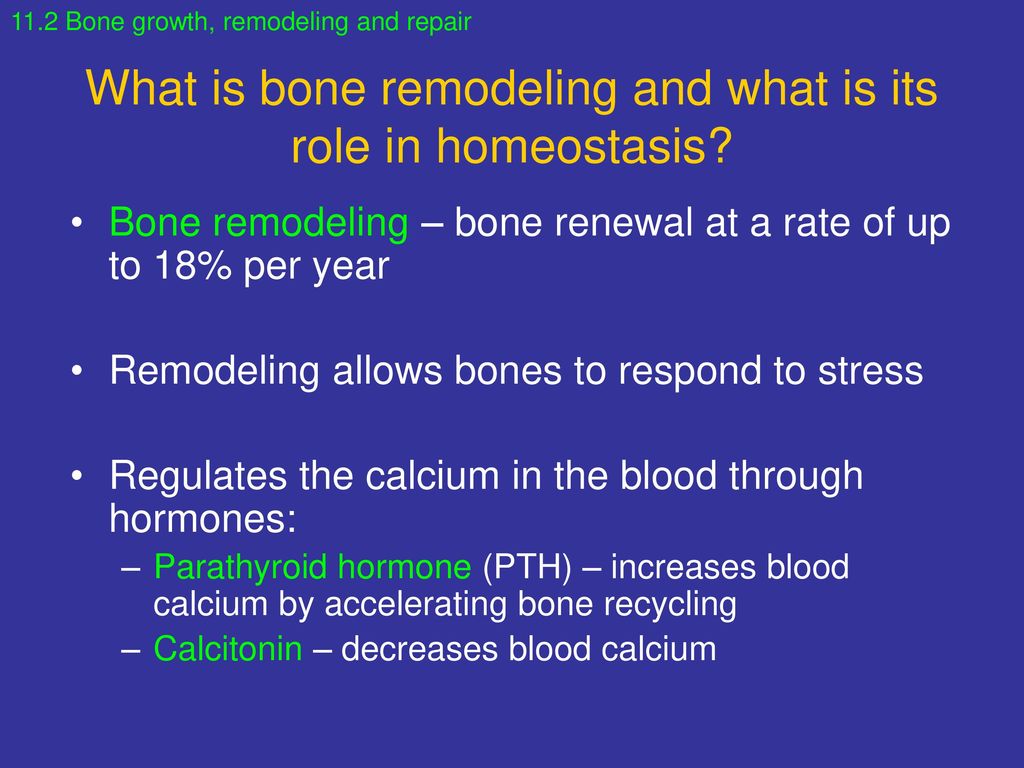
Bone Remodeling. Even after skeletal maturity has been attained, bone is constantly being resorbed and replaced with new bone in a process known as bone remodeling. In this lifelong process, mature bone tissue is continually turned over, with about 10 percent of the skeletal mass of an adult being remodeled each year.

7.5: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair Biology Diagrams
This page titled 14.5: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Suzanne Wakim & Mandeep Grewal via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.

The purpose of bone remodeling is to regulate calcium homeostasis, repair micro-damage to bones from everyday stress, and to shape the skeleton during growth. Bone growth factors affect the process of bone remodeling. These factors include insulin-like growth factors I and II, transforming growth factor beta, fibroblast growth factor, platelet

14.5: Bone Growth, Remodeling, and Repair Biology Diagrams
This process of skeletal change is known as bone remodeling, which both protects the structural integrity of the skeletal system and metabolically contributes to the body's balance of calcium and phosphorus. Osteoblast cells contribute to bone growth and derive from mesenchymal origin. Mesenchymal cells are stem cells that can differentiate